Last updated on January 28th, 2024 at 07:59 am
Bowel Obstruction (intestinal obstruction) is a condition wherein there is a blockage that prevents food or fluid from entering either the small intestines ( small bowel obstruction ) or the large intestines.
Reasons for bowel obstruction may precipitate due to fibrous tissue development (adhesions) after abdominopelvic surgery; hernias; colon cancer; some medications; or inflammatory bowel conditions with corresponding strictures of surrounding structures such as Crohn’s disease, and diverticulitis.
Prompt management of bowel obstruction is reversible and can be successfully treated. However, without treatment, the blocked parts of the intestine will die, and thereby cause serious medical problems.
Signs and Symptoms of Bowel Obstruction
Clinical manifestations of bowel obstruction are as follows:
- Abdominal cramps, with pain commonly that comes and goes
- Loss of appetite
- Constipation
- Vomiting
- Difficulty in passing bowels or gas
- Swelling of the abdomen
- Diarrhea, with associated partial blockage
Causes and Risk Factors of Bowel Obstruction
There are two major types of intestinal obstruction and are termed partial blockage or complete blockage. Common causes of bowel obstruction vary for adults and children and may include the following:
For adults:
- Intestinal adhesions – The formation of fibrous tissues in the abdomen, prominently forming after abdominopelvic surgery.
- Hernias
- Colon cancer
For children:
- Intussusception – A condition characterized by the telescoping of the intestines.
Other causes are mentioned below:
- Inflammatory bowel disease (e.g., Crohn’s disease)
- Diverticulitis – A condition characterized by small and bulging pouches (diverticula) in the digestive tract that may become inflamed or infected.
- Twisting of the colon, otherwise called volvulus
- Impacted feces
A subtype called intestinal pseudo-obstruction, otherwise known as paralytic ileus, is characterized as having the clinical manifestations of intestinal obstruction without physical blockage present in the digestive tract.
It is described as a problem of the nerves or muscle of the intestines and is thereby prohibiting coordinated and effective contractions for the proper movement of food and fluids. It can affect any part of the intestine and reasons of occurrence may include:
- Surgery in the abdomen or pelvis
- Infection
- Certain medications (e.g., Opioids)
- Muscle and nerve disorders (e.g., Parkinson’s disease)
Risk factors to bowel obstruction usually are associated with the following:
- Surgery in the abdominopelvic area
- Crohn’s disease
- Diverticulitis
- Hernia
- Colon cancer
- Stomach cancer
- Ovarian cancer
- Scar tissue from surgery in the abdominopelvic area
- Radiation therapy in the abdomen
- Metastatic cancer of the breast, lung and melanoma that migrated to the abdomen
Diagnosis of Bowel Obstruction

Diagnosing bowel obstruction will include a combination of tests and procedures and they are:
- Physical exam – This starts with a comprehensive medical history of the symptoms followed by a physical exam, focusing on assessment for swelling or lump in the abdomen, and auscultation for bowel sounds.
- X-ray – An abdominal x-ray will be ordered to illuminate the bowels and visualize obstructions.
- Computerized tomography – or a CT scan may be warranted for obstructions otherwise not seen when x-ray was used.
- Ultrasound – This method is better suited for children, especially when diagnosing bowel obstruction caused by intussusception wherein it will show a bull’s-eye image.
- Air or barium enema – This allows for enhanced and better visualization of the blocked intestines. For children with intussusception, the air or barium enema can address the condition most of the time, thereby limiting further treatment needed.
Bowel Obstruction Nursing Diagnosis
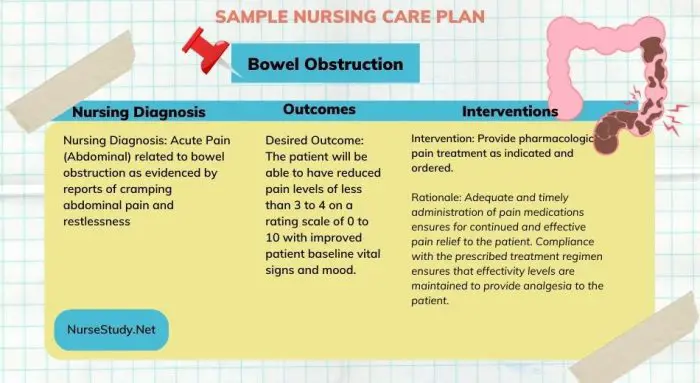
Bowel Obstruction Nursing Care Plan1
Acute Pain (Abdominal)
Nursing Diagnosis: Acute Pain (Abdominal) related to bowel obstruction as evidenced by reports of cramping abdominal pain and restlessness
Desired Outcome: The patient will be able to have reduced pain levels of less than 3 to 4 on a rating scale of 0 to 10 with improved patient baseline vital signs and mood.
Bowel Obstruction Nursing Interventions
Anticipate occurrence through providing measures to relieve pain, especially before it becomes severe. Anticipating occurrence and episodes of severe pain will provide continued relief to the patient. Timely pain assessment ensures for the patient to have controlled pain levels and for the continuity of activities of daily living.
Provide cognitive-behavioral therapy of the patient’s pain through the following:
● Distraction such as watching TV, reading, etc.
● Eliciting the relaxation response such as directed meditation, deep breathing, etc.
● Guided imagery
Providing cognitive-behavioral therapy provides comfort by changing the patient’s perception to pain. Distraction techniques help with pain control by lessening the patient’s perception of pain.Increased stress levels are related to the increase in pain levels. Invoking the relaxation response may decrease the effects of stress on pain.Guided imagery such as using mental pictures or relaxing events will help the patient to be distracted from pain.
Offer cutaneous stimulation or physical interventions through the following:
● Heat and cold applications
● Contralateral stimulation
● Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) Cutaneous stimulation may provide temporary pain relief through tactile stimulation.
Cold is effective in reducing pain by decreasing the release of pain-inducing chemicals while heat is helpful by improving blood flow and reduction of pain impulses.This technique is used when touching the painful area and is done by stimulating the skin opposite the painful area. This method may be used to apply low-volt electricity over painful areas and thereby temporarily the pain pathways, thereby providing pain relief.
Provide pharmacologic pain treatment as indicated and ordered. Adequate and timely administration of pain medications ensures for continued and effective pain relief to the patient. Compliance with the prescribed treatment regimen ensures that effectivity levels are maintained to provide analgesia to the patient.
Perform nursing care at the peak levels of pain medications. Careful scheduling of tasks during peaks of effectivity of pain medications ensures for optimal client comfort and compliance to care.
Bowel Obstruction Nursing Care Plan 2
Nursing Diagnosis: Constipation related to bowel obstruction as evidenced by abdominal distention, infrequent passage of stools and associated pain with defecation.
Desired Outcome: The patient will be able to verbalize relief from the discomfort of constipation and maintain passage of soft and formed stools in regular intervals, normal to the patient.
Bowel Obstruction Nursing Interventions
Check and assess the usual pattern of bowel movement of the patient, to include the frequency and consistency. Establishing baseline data of the bowel patterns of the patient ensures for the accurate and timely recognition of deviations, specifically manifestations of constipation.
Consider the patient’s laxative and enema usage, including the type and frequency. Laxative abuse plays a big role in the development of constipation. Laxative dependency can cause the muscles and innervations of the intestine to inadequately produce the urge to defecate. Because of this, the colon will not respond normally to the presence of stool and therefore inhibit elimination.
Investigate the patient’s usual dietary habits, including eating habits, schedule, and fluid intake. Interruption to usual meal schedules, the type of food taken, and inadequate fluid intake can cause constipation.
Assess the patient’s activities of daily living. A sedentary lifestyle consisting of inadequate exercise regimen and prolonged bed rest can contribute to constipation development.
Take note of the patient’s current medications. Various medications can alter the normal peristalsis, or intestinal movement, and thereby cause constipation. Drugs such as opioids, antidepressants, antihypertensives and anticholinergics are some examples that may affect the gut.
Assess for the fear of pain with bowel elimination. Certain conditions such as hemorrhoids, and other anorectal disorders are painful and may cause the patient to withhold defecating. Over time, this results in a dilated rectum that no longer is triggered by stool presence for bowel elimination.
Bowel Obstruction Nursing Care Plan 3
Imbalanced Nutrition: Less Than Body Requirements
Nursing Diagnosis: Imbalanced Nutrition: Less Than Body Requirements related to bowel obstruction as evidenced by changes in bowel functions and imbalances in nutritional studies.
Desired Outcome: The patient will be able to recover appropriate and normal laboratory results with no further observed signs of malnutrition.
Bowel Obstruction Nursing Interventions
Ensure measuring of the patient’s daily calorie intake. Utilizing a record of the patient’s food intake will help the healthcare providers in assessing patient needs, deficiencies and other nutritional patterns that are crucial for management of the patient’s malnutrition.
Weigh daily or as ordered. Make sure to take note of weight history and skinfold measurements. Although patient daily weighing is limited in assessing for malnutrition, it is still necessary to allow for proper assessment. Skinfold measurement ensures for proper assessment of latent fat reserves of the patient and in determining muscle or fat wasting.
Encourage patients to eat small, frequent meals as tolerated. Because of the manifestations of bowel obstruction, (e.g., abdominal pain, bloatedness), eating for the patient could be difficult. Having the patient eat small, frequent meals guarantees the patient of continuous nutritional intake.
Monitor laboratory studies, especially serum albumin, transferrin, WBC and RBC counts, serum electrolytes. Laboratory tests assist in determining the patient’s medical status. Monitoring for decreasing levels of albumin (below 3.8 g/dl) may suggest protein reduction in the body. Depressed WBC and RBC counts also may indicate malnutrition and reduced infection resistance and anemia. Elevated serum potassium and decreased sodium levels may also indicate malnutrition.
Look for physical manifestations of poor intake. The patient with nutritional deficiencies will appear fatigued and will have sluggish responses. The patient may also have pale and dry skin, decrease attention span and swollen and red mucus membranes. Tachycardia and hypertension may be present for patients with malnutrition.
Bowel Obstruction Nursing Care Plan 4
Nursing Diagnosis: Ineffective Coping related to unpredictable nature of disease process secondary to bowel obstruction as evidenced by verbalization of inability to cope and poor self-esteem.
Desired Outcome: The patient will be able to identify, acknowledge and utilize applicable coping mechanisms with regards to his current condition.
Bowel Obstruction Nursing Interventions
Assess the patient and significant others’ knowledge and understanding of the disease. Establishing baseline assessment of the expectations and understanding of the patient and his family will help the healthcare provider to address problems realistically. Anxiety and any misconceptions may hinder health teaching and learning for the patient.
Determine the external stressors of the patient. (Social environment, relationships, etc.). Stress can directly affect the immune system of the patient and their response to treatment regimen. External stressors are powerful enough to hinder the treatment goals of the patient and should be addressed accordingly.
Consider opportunities for the patient to discuss other aspects of their life (e.g., sexual needs) that is hindered by the disease. Stress brought about by illness can affect all aspects of a person’s life. Allowing for patient verbalization of concerns ensures the patient that they are heard and can be assisted with.
Assist the patient in identifying personal and effective coping skills. Using previously successful coping skills can help the patient handle and manage their current situation and strategize for future issues.
Ensure that the patient has adequate and uninterrupted sleep and rest. Illness can be exhausting for the patient. Interruptions with established rest and sleep patterns may further aggravate the patient’s coping abilities.
Encourage use of relaxation techniques, deep-breathing exercises, etc. These methods assist in refocusing the patient’s attention, thereby inducing relaxation, and coping with the disease.
Bowel Obstruction Nursing Care Plan
Nursing Diagnosis: Deficient Knowledge related to information misinterpretation of the disease secondary to bowel obstruction as evidenced by statements of misconceptions and development of preventable complications.
Desired Outcome: The patient will be able to verbalize understanding of the disease and its associated complications and effectively participate in the treatment regimen.
Bowel Obstruction Nursing Interventions
Ascertain the patient’s perception of the disease. This ensures the healthcare provider of a baseline assessment and insight of the educational and coping needs of the patient.
Look at the disease process, cause and effect that reduce or aggravate the patients’ symptoms. Encourage the patient to verbalize concerns. Precipitating factors vary for every patient. Allowing the patient to realize factors that may reduce or worsen their symptoms enables them to have accurate knowledge of the disease. With these, the patient is empowered to take sound decisions when it comes to their care.
Review the patient’s medication regimen, including the indication, frequency, and dosage. Also take note of associated side effects of the drugs administered. Explaining this to the patient promotes understanding, thereby gaining their trust and cooperation with the treatment regimen.
Highlight the importance of proper handwashing techniques and perineal care. Good skin care ensures reduction of latent bacteria flora and reduces risk of skin irritation and breakdown that can develop to infections.
Recommend smoking cessation. Smoking may worsen current symptoms and may be contraindicated for the patient’s treatment regimen.
Highlight the need for periodic follow-ups and long-term reevaluation of the condition. Some causes of bowel obstruction predispose a patient to other conditions, such as increased risk for colon cancer. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can ensure early prevention and detection of developing disease.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the common causes of bowel obstruction?
Bowel obstruction can be caused by a variety of conditions, including adhesions, hernias, tumors, inflammatory bowel disease, diverticulitis, and volvulus.
Other factors that may contribute to bowel obstruction include intestinal twisting or kinking, intussusception, and impacted feces.
- What are the signs and symptoms of bowel obstruction?
The signs and symptoms of bowel obstruction can vary depending on the location and severity of the obstruction, but commonly include abdominal pain and cramping, bloating, nausea and vomiting, constipation or diarrhea, inability to pass gas, and loss of appetite. In severe cases, patients may also experience fever, dehydration, and shock.
- What is the nursing management for patients with bowel obstruction?
The nursing management for patients with bowel obstruction includes assessing and monitoring the patient’s vital signs, providing supportive care, administering IV fluids and electrolytes, monitoring laboratory values, and preparing the patient for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures.
The nurse should also educate the patient and family about the condition, provide emotional support, and assist with discharge planning and follow-up care. In some cases, the patient may require surgery or other advanced interventions, which will require close collaboration with the healthcare team. The nurse should also closely monitor for complications such as bowel perforation, sepsis, or shock and intervene promptly if necessary.
Nursing References
Ackley, B. J., Ladwig, G. B., Makic, M. B., Martinez-Kratz, M. R., & Zanotti, M. (2020). Nursing diagnoses handbook: An evidence-based guide to planning care. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier. Buy on Amazon
Gulanick, M., & Myers, J. L. (2017). Nursing care plans: Diagnoses, interventions, & outcomes. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier. Buy on Amazon
Ignatavicius, D. D., Workman, M. L., Rebar, C. R., & Heimgartner, N. M. (2018). Medical-surgical nursing: Concepts for interprofessional collaborative care. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier. Buy on Amazon
Silvestri, L. A. (2020). Saunders comprehensive review for the NCLEX-RN examination. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier. Buy on Amazon
Disclaimer:
Please follow your facility’s guidelines, policies, and procedures.
The medical information on this site is provided as an information resource only and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes.
This information is intended to be nursing education and should not be used as a substitute for professional diagnosis and treatment.



Anna C., Thank you and God bless you. This was simple and straight to the point. Very helpful. Continue the good work.
GREAT!!!
great! thank you and god bless
Wonderful information here. Thank you. Saved me much time on my clinical paperwork!