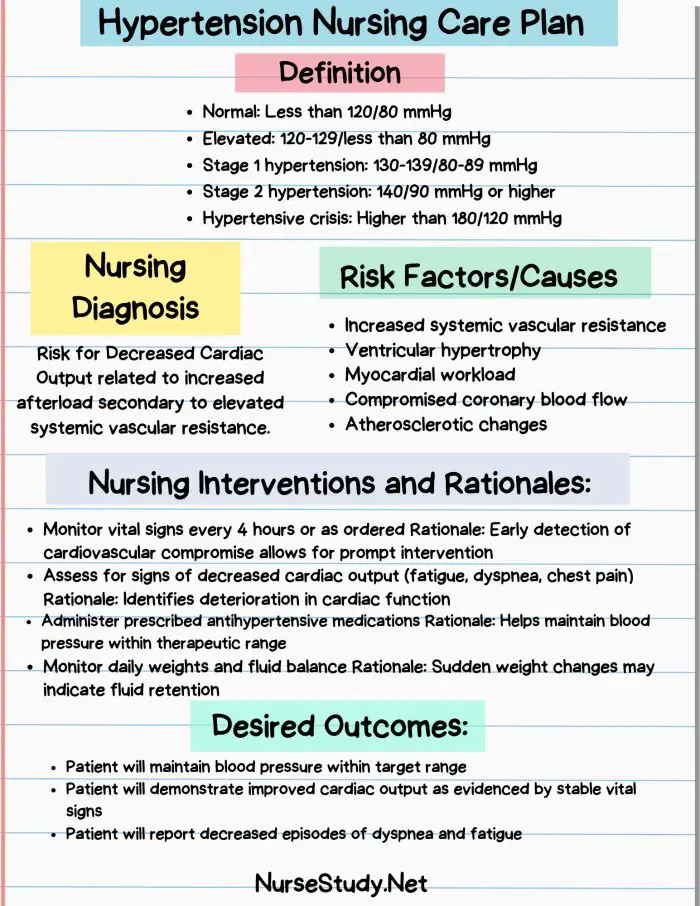
Hypertension, commonly called high blood pressure, is a condition where the force of blood pushing against the artery walls stays higher than normal over time. Most people don’t feel any symptoms, which is why it’s often called the “silent killer.” If left untreated, hypertension can damage the heart, brain, kidneys, and other organs.
For nurses, recognizing hypertension early and creating an effective care plan is essential to prevent complications like heart attacks, strokes, and kidney failure. This article explains hypertension in simple terms, outlines the main nursing diagnoses, and provides five complete care plans with rationales based on the latest NANDA-I 2024–2026 guidelines.
Pathophysiology & Causes
How Hypertension Develops
Blood pressure is determined by cardiac output (how much blood the heart pumps) and systemic vascular resistance (how tight or relaxed the blood vessels are). In hypertension, one or both stay elevated. Over time, this constant high pressure damages the arteries and forces the heart to work harder.
Two Main Types
- Primary (Essential) Hypertension – No single cause; develops gradually due to genetic factors and lifestyle habits.
- Secondary Hypertension – Caused by another condition, such as kidney disease, hormonal disorders, or certain medications.
Common Risk Factors
- Family history of hypertension
- High-sodium diet
- Lack of physical activity
- Overweight or obesity
- Smoking and alcohol overuse
- Chronic stress
- Diabetes or high cholesterol
Signs & Symptoms
Common (Often Mild or No Symptoms)
- Headache, especially in the morning
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Nosebleeds (occasional)
Urgent (Hypertensive Crisis or Complications)
- Severe headache
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Confusion or difficulty speaking
- Weakness or numbness on one side of the body
- Vision loss
- Seizures
Note: Many people feel completely normal even when their blood pressure is dangerously high. Regular screening is key.
Nursing Assessment
Subjective Data (What the Patient Reports)
- Headaches, dizziness, or blurred vision
- Chest discomfort or palpitations
- Shortness of breath with activity
- Fatigue or weakness
- Diet high in salt or processed foods
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Smoking or alcohol use
- Stress or poor sleep
Objective Data (What the Nurse Observes/Measures)
- BP readings consistently ≥130/80 mmHg
- Heart rate changes (tachycardia or bradycardia depending on meds)
- Retinal changes on eye exam (e.g., narrowed vessels)
- Edema in ankles or feet
- Abnormal heart sounds (S4 gallop)
- Weight gain from fluid retention
- Abnormal lab results (elevated creatinine, cholesterol)
Nursing Diagnosis for Hypertension (NANDA-I)
Based on assessment data, the following nursing diagnoses are commonly used for patients with hypertension:
- Decreased Cardiac Output
- Deficient Knowledge (Hypertension Management)
- Excess Fluid Volume
- Risk for Unstable Blood Pressure
- Sedentary Lifestyle
Nursing Goals & Outcomes
Short-Term Goals
- Blood pressure reduced to a safe range before discharge
- Patient verbalizes understanding of medication regimen and lifestyle changes
- Relief from any hypertension-related symptoms
Long-Term Goals
- Maintain blood pressure within target range (<130/80 mmHg)
- Consistent medication adherence
- Lifestyle changes maintained for at least 6 months
- No development of hypertension-related complications
Nursing Care Plans with Rationales
1. Decreased Cardiac Output
Nursing Diagnosis: Decreased Cardiac Output related to increased systemic vascular resistance secondary to chronic hypertension as evidenced by elevated BP readings (155/95 mmHg), S4 heart sound, and patient report of fatigue.
Goals/Outcomes:
- BP within target range within 48 hours of treatment
- Regular heart rate and rhythm
- No dizziness or chest pain
Interventions with Rationales:
- Monitor BP and heart rate every 4 hours – Detects changes in cardiac status early.
- Administer antihypertensives as prescribed – Lowers vascular resistance, improving cardiac output.
- Encourage rest during acute BP elevation – Reduces heart workload.
- Monitor intake/output and edema – Identifies fluid overload affecting cardiac output.
- Elevate head of bed if shortness of breath present – Improves lung expansion and oxygenation.
Evaluation:
BP improved to 132/84 mmHg, heart rate 80 bpm, no dizziness or chest pain.
2. Deficient Knowledge (Hypertension Management)
Nursing Diagnosis: Deficient Knowledge related to lack of exposure to information about hypertension and its treatment as evidenced by patient stating, “I don’t think I need medication since I feel fine.”
Goals/Outcomes:
- Patient explains hypertension in their own words before discharge
- Patient lists at least 3 lifestyle changes for BP control
- Patient demonstrates correct home BP monitoring technique
Interventions with Rationales:
- Assess current understanding of hypertension – Establishes a teaching starting point.
- Provide education on disease process and risks – Improves awareness of consequences.
- Review medication names, purposes, and side effects – Increases adherence.
- Demonstrate home BP monitoring – Promotes self-management.
- Use teach-back method – Confirms understanding.
Evaluation:
Patient demonstrated BP monitor use and stated, “I need to take my meds even if I feel okay.”
3. Excess Fluid Volume
Nursing Diagnosis: Excess Fluid Volume related to excessive sodium intake and decreased kidney function as evidenced by 2 kg weight gain in 3 days, +2 pitting edema, and BP 160/98 mmHg.
Goals/Outcomes:
- Edema reduced to trace or none
- BP reduced to <140/90 mmHg
- Balanced intake and output
Interventions with Rationales:
- Monitor daily weights – Detects fluid changes early.
- Assess edema and lung sounds – Identifies fluid overload progression.
- Administer diuretics as ordered – Removes excess fluid and sodium.
- Restrict sodium in diet – Prevents further fluid retention.
- Educate on reading food labels – Empowers patient to make low-sodium choices.
Evaluation:
Weight decreased by 1.5 kg in 2 days, edema resolved, BP 138/88 mmHg.
4. Risk for Unstable Blood Pressure
Nursing Diagnosis: Risk for Unstable Blood Pressure related to inconsistent medication adherence and high-sodium diet.
Goals/Outcomes:
- Maintain stable BP within target range throughout hospitalization
- Identify and avoid BP fluctuation triggers
Interventions with Rationales:
- Monitor BP at regular intervals – Detects fluctuations promptly.
- Review medication schedule and reinforce adherence – Prevents peaks and troughs in BP.
- Limit caffeine and high-sodium foods – Reduces BP variability.
- Teach relaxation techniques – Lowers stress-related BP spikes.
- Collaborate with healthcare team on med adjustments – Ensures stable control.
Evaluation:
BP remained between 125/78 mmHg and 134/84 mmHg during the stay.
5. Sedentary Lifestyle
Nursing Diagnosis: Sedentary Lifestyle related to lack of knowledge about benefits of exercise as evidenced by patient report of no regular activity and BMI of 31.
Goals/Outcomes:
- Patient begins walking 15 minutes daily within 1 week
- Gradually increase to 30 minutes most days over 3 months
Interventions with Rationales:
- Assess activity preferences – Increases likelihood of adherence.
- Set realistic activity goals – Builds confidence and gradual progress.
- Educate on exercise benefits for BP control – Motivates participation.
- Encourage incorporating activity into routine – Improves sustainability.
- Provide community resources for safe exercise – Removes barriers.
Evaluation:
Patient began 15-minute walks and reported feeling more energetic after one week.
Patient Education
Know Warning Signs: Seek immediate help for chest pain, sudden weakness, vision changes, or severe headache. Through treatment, patients with hypertension can achieve better control of their blood pressure and significantly reduce their risk of complications. Empowering the patient with knowledge and resources is one of the most important roles of the nurse in hypertension care.
Medication Adherence: Take medications exactly as prescribed; do not stop suddenly.
Diet: Follow a DASH or low-sodium diet; limit processed foods.
Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate activity per week.
Home Monitoring: Check BP regularly and record results.
Avoid Risk Factors: Stop smoking, limit alcohol, and manage stress.
References
- Ackley, B. J., Ladwig, G. B., Makic, M. B., Martinez-Kratz, M. R., & Zanotti, M. (2023). Nursing diagnoses handbook: An evidence-based guide to planning care. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier.
- Egan BM, Zhao Y, Axon RN. US trends in prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension, 1988-2008. JAMA. 2010 May 26;303(20):2043-50. doi: 10.1001/jama.2010.650. PMID: 20501926.
- Harding, M. M., Kwong, J., & Hagler, D. (2022). Lewis’s Medical-Surgical Nursing: Assessment and Management of Clinical Problems, Single Volume. Elsevier.
- Herdman, T. H., Kamitsuru, S., & Lopes, C. (2024). NANDA International Nursing Diagnoses – Definitions and Classification, 2024-2026.
- Ignatavicius, D. D., Rebar, C., & Heimgartner, N. M. (2023). Medical-Surgical Nursing: Concepts for Clinical Judgment and Collaborative Care. Elsevier.
- Oparil S. Women and hypertension: what did we learn from the Women’s Health Initiative? Cardiol Rev. 2006 Nov-Dec;14(6):267-75. doi: 10.1097/01.crd.0000240530.94242.0c. PMID: 17053372.
- Muntner P, Hardy ST, Fine LJ, Jaeger BC, Wozniak G, Levitan EB, Colantonio LD. Trends in Blood Pressure Control Among US Adults With Hypertension, 1999-2000 to 2017-2018. JAMA. 2020 Sep 22;324(12):1190-1200. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.14545. PMID: 32902588; PMCID: PMC7489367.
- Silvestri, L. A. (2023). Saunders comprehensive review for the NCLEX-RN examination. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier.